I didnt know it had that much of an impact. Another reason to abolish cars for all but the most necessary services.
It’s the same with rotors and brake dust. Idk where people think that stuff goes when they’re worn out. All people know is exhaust emissions but non exhaust emissions are doing untold damage too.
Asbestos frikkin’ everywhere
They don’t use asbestos any more.
And how has that removed the existing decades of contamination?
Some use copper, which can kill fish when it washes into rivers. Iirc some states have banned copper in brake pads but not all.
Still was used up until recently in many parts of the world. Most, if not almost all, pre fabricated buildings constructed before 2008 in South Africa are made of asbestos. And many of these buildings, including classrooms, are still standing and in use today. I went to school in asbestos made classrooms and I’m only in my mid 20s. I know someone who currently teaches at a school with prefabricated classrooms likely made of asbestos.
deleted by creator
50 years ago was the 1970s lol
Oh boy I’m sure glad electric cars are the future!

Most of them are heavier than cars with petrol/gas engines too due to the batteries, so electric cars, on average, will need even bigger tyres that wear more.
ZYBERTRUKKKS doing EPIC peelouts in treat dispensing parking lots will save humanity

I can’t get the article to load, but I imagine this is the result of storm drains taking runoff directly from roadways into waterways, not particles blowing through the air and landing in the sea. Seems like it’s past time to stop putting unfiltered water into waterways after it’s been contaminated by human activities.
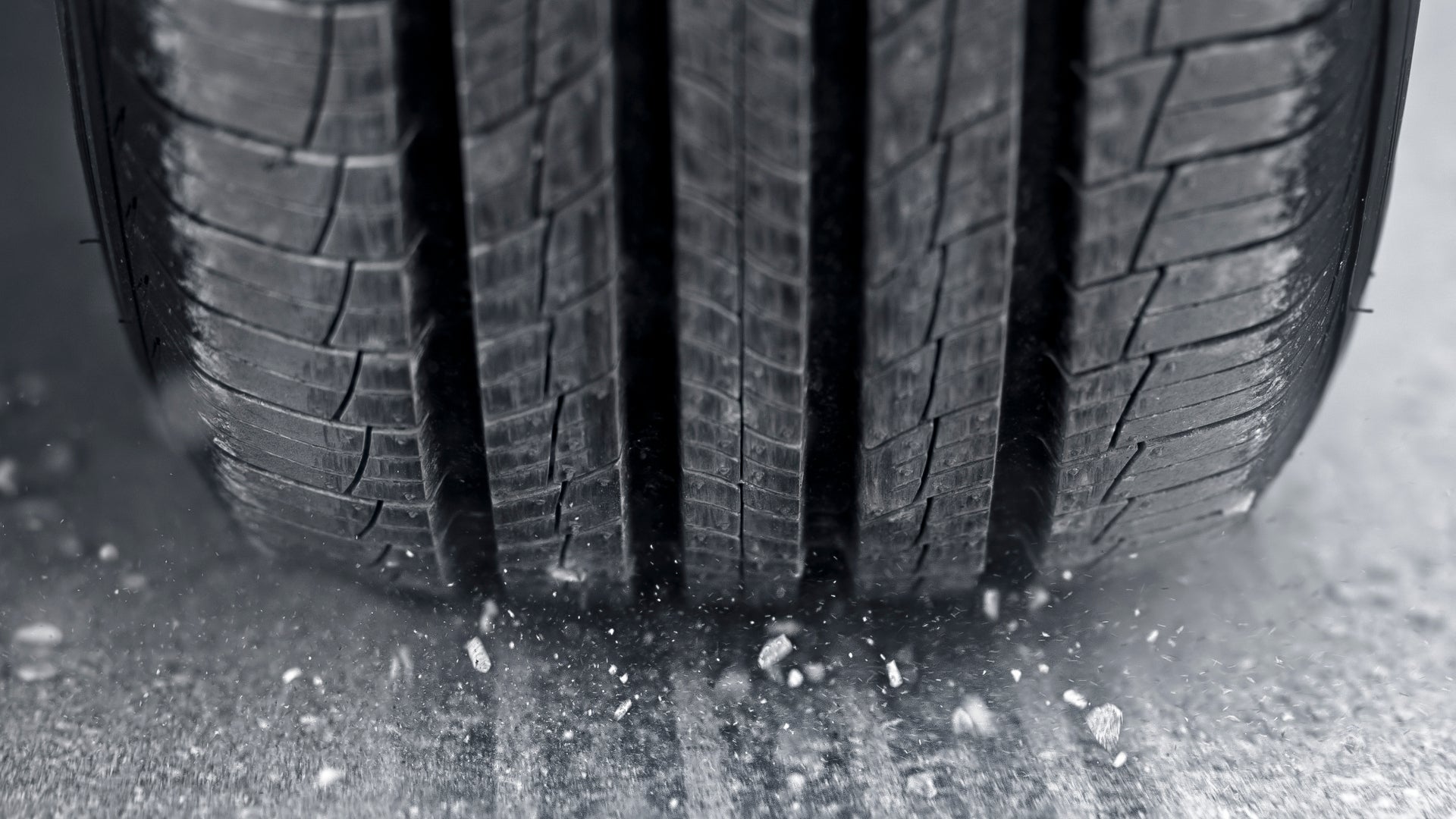
When contemplating the emissions from road vehicles, our first thought is often about the various gases coming out of the tailpipe. However, new research shows that we should be more concerned with the harmful particles that are shed from tires and brakes.
Scientists have a good understanding of engine emissions, which typically consist of unburnt fuel, oxides of carbon and nitrogen, and particulate matter related to combustion. However, new research shared by Yale Environment 360 indicates that there may be a whole host of toxic chemicals being shed from tires and brakes that have been largely ignored until now. Even worse, these emissions may be so significant that they actually exceed those from a typical car’s exhaust output.
A research paper published in 2020 highlighted the impact of tire pollution by examining the plight of coho salmon in West Coast streams. Scientists eventually identified a chemical called 6PPD, typically used in tire manufacturing to slow cracking and degradation. When exposed to ozone in the atmosphere, the chemical transforms into multiple other species, including 6PPD-quinone—which was found to be highly toxic to multiple fish, including coho salmon. The same chemical has since been detected in human urine, though any potential health impacts remain unknown.
The discovery of 6PPD-q and its impact has brought new scrutiny to the pollution generated by particles shedding from tires and brakes. In particular, tire rubber is made up of over 400 different chemical compounds, many of which are known to have negative effects on human health. Tire Dust Makes Up the Majority of Ocean Microplastics, Study Finds Particulate emissions from tires—and, to a lesser extent, brakes—are becoming a new focus for researchers looking into automobile pollution.
New research efforts are only just beginning to reveal the impact of near-invisible tire and brake dust. A report from the Pew Charitable Trust found that 78 percent of ocean microplastics are from synthetic tire rubber. These toxic particles often end up ingested by marine animals, where they can cause neurological effects, behavioral changes, and abnormal growth.
Meanwhile, British firm Emissions Analytics spent three years studying tires. The group found that a single car’s four tires collectively release 1 trillion “ultrafine” particles for every single kilometer (0.6 miles) driven. These particles, under 100 nanometers in size, are so tiny that they can pass directly through the lungs and into the blood. They can even cross the body’s blood-brain barrier. The Imperial College London has also studied the issue, noting that "There is emerging evidence that tire wear particles and other particulate matter may contribute to a range of negative health impacts including heart, lung, developmental, reproductive, and cancer outcomes.”
It’s an emissions problem that won’t go away with the transition to EVs, either. According to data from Emissions Analytics, EVs tend to shed around 20 percent more from their tires due to their higher weight and high torque compared to traditional internal combustion engine-powered vehicles.
Indeed, the scale of these emissions is significant. Particulate emissions from tires and brakes, particularly in the PM2.5 and PM10 size ranges, are believed to exceed the mass of tailpipe emissions from modern vehicle fleets, as per a study published in Science of the Total Environment this year.
This issue has largely flown under the radar until recently. Tailpipe emissions are easy to study, simply requiring the capture or sensing of gases directly at the engine’s exhaust. Capturing the fine particulates emitted from tires and brakes is altogether more difficult. Doing so in a way that accurately reflects the quantity of those emissions is yet harder. Such pollution is perhaps unlikely to have a direct impact on issues like climate change, but the potential toxicity for humans, animals, and the broader environment is a prime concern.
Regulators are already scrambling to tackle this issue, heretofore largely ignored by governments around the world. In the EU, the Euro 7 standards will regulate tire and brake emissions from 2025. In the U.S., the California EPA will require tire manufacturers to find an alternative chemical to 6PPD by 2024, to help reduce 6PPD-q entering the environment going forward. In turn, manufacturers are exploring everything from alternate tire compositions to special electrostatic methods to capture particulate output.
Expect this issue to gain greater prominence in coming years as regulators have more accurate data to act upon. There is great scope to slash this form of pollution if we properly understand the impacts of our cars in full.
Expect this issue to gain greater prominence in coming years as regulators have more accurate data to act upon. There is great scope to slash this form of pollution if we properly understand the impacts of our cars in full.
 and related
and related  will call that turbo communism, their credulous cults will agree, and chances are those regulations won’t meaningfully happen
will call that turbo communism, their credulous cults will agree, and chances are those regulations won’t meaningfully happen 
It’s an emissions problem that won’t go away with the transition to EVs, either. According to data from Emissions Analytics, EVs tend to shed around 20 percent more from their tires due to their higher weight and high torque compared to traditional internal combustion engine-powered vehicles.
This is exactly why a ton of modern day emissions regulations make no sense. A heavier object obviously takes more energy to move and puts more wear on it’s components, which cause their own pollution (like the tyre microplastics). And modern EVs just seem to be getting heavier and heavier, with stupidly powerful engines for what they are. Seriously, what ordinary sized car needs more than 100kw or 140 horsepower? That’s plenty for cruising at even highway speeds. What ordinary car needs to weigh two metric tons?
You want less emissions and energy used? Make the damn things lighter!
Burgerland is an arms race where no red-blooded Burgerlander wants to have the small vehicle because then they’d feel weak.

Also because small car = die in crash to suburbatank :(
Kill or be killed fits Burgerland vibes for sure

I’m not surprised, yet also the AMOUNT is shocking.
Genuinely surprised it wasn’t polyester in the wash, I also didn’t realise there was so much plastic in rubber

Rubber is plastic - it’s just a plastic that is softer at room temperature.
deleted by creator

ban cars
what about rubber tired metros and translohr?
I was sure it would be fishing nets.
Lmao hoooly shit ban cars


😋
lmao check out this whiteboy swag
tires are so underpowered that they can’t even pollute rainwater, git gud