- cross-posted to:
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- cross-posted to:
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
cross-posted from: https://lemmy.world/post/19446697
This has scam written all over it. Might as well throw in a monorail.
I hear those things are awfully loud.
It glides as softly as a cloud.
Is there a chance the track could bend?
Not on your life, my Feddit friend.
What about us braindead slobs?
You’ll be given cushy jobs!
Were you sent here by the devil?
Absolutely. Another deranged idea from another idiot asshole from the techbro community.
Literally the opposite of what Mr Burns did.
Because that won’t fuck with nocturnal animals at all….
Who cares about the environment! We have investors to grift! Money to be made!
It won’t actually work. So yes, this is just a grift until funding dries up.
In the demo, former SpaceX intern and startup cofounder Ben Nowack is shown using an app outside in the dark that seems to control the location of the company’s sunlight-reflecting mirrors. As he selects the spot where he stands, the area around him is suddenly illuminated as if by stadium lights.
LMAO of course it’s a SpaceX intern’s idea.
Yeah, it’s boring.
I want a Starliner intern to come up with something.
Btw, Starliner undocked the space station, set course back to earth and must have landed, uncrewed, 2 - 3 hours ago. That was the plan, at least.
Edit: Here it is after undocking the station, showing off it’s glorious thrusters:
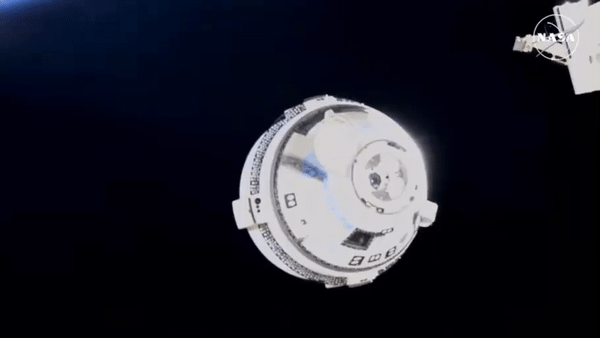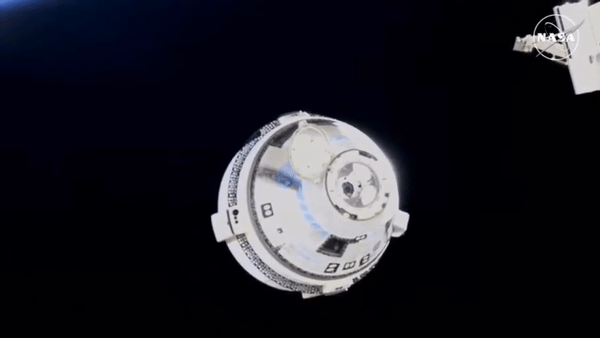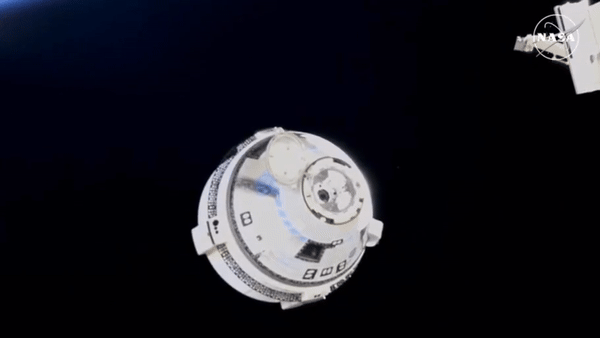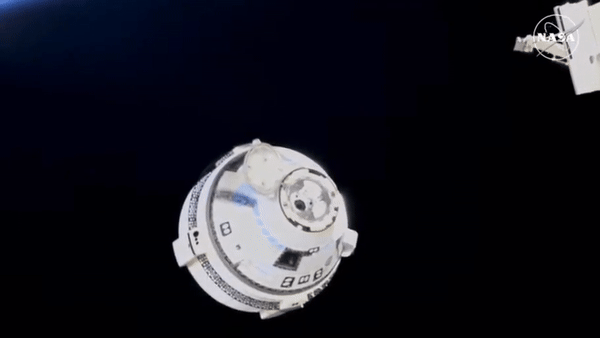
Hasn’t made it to re-entry burn yet. That’s scheduled for about 40 minutes from now. Is supposed to land around 10 pm New Mexico time. Or about 2 hours from now.
The touchdown

Seems like both Astronauts would have made a safe return after all.
To be fair, if I’m NASA, who’s had two fatal incidents with known damaged spacecraft, I’m also not sending two astronauts down on a known damaged spacecraft.
You’re right, i must have worded it completely wrong, because i think it was the best decision NASA could have made.
I guess it’s good for Boeing that Starliner made the way back home without incidents and had a smooth landing, but i really don’t know,l. If i were NASA, i wouldn’t spend more money on this. In the end only they know if Boeing is capable of finishing this. I think it depends on all those tests Boeing made being analyzed. They, probably, will then present NASA their conclusions and how they plan to proceed from there.
Maybe Starliner’s AI is conscious, doesn’t like humans and starts sabotaging itself when humans are onboard.
it’s a SpaceX intern’s idea.
It’s older than that.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_mirror_(climate_engineering)
Space mirrors are satellites that are designed to change the amount of solar radiation that impacts the Earth as a form of climate engineering. The concept was first theorised in 1923 by physicist Hermann Oberth[1][2][3][4] and later developed in the 1980s by other scientists.[5] Space mirrors can be used to increase or decrease the amount of solar energy that reaches a specific point of the earth for various purposes. They have been theorised as a method of solar geoengineering by creating a space sunshade to deflect sunlight and counter global warming.[5][6]
There have been several proposed implementations of the space mirror concept but none have been implemented thus far other than the Znamya project by Russia due to logistical concerns and challenges of deployment.[5][7]
The Znamya project was a series of orbital mirror experiments in the 1990s that intended to beam solar power to Earth by reflecting sunlight. It consisted of three experiments the Znamya 1, Znamya 2 experiment, and the failed Znamya 2.5. The Znamya 1 was a ground experiment that never was launched.[17] The Znamya 2 was the first successful launch the Znamya project had. It was attached to the unmanned Progress M-15.[17]The deployment resulted in a bright light of a width of 5km and with the intensity of a Full Moon being shined.[17] The Znamya 3 was proposed but never acted upon because of the failure of the Znamya 2.5.[17] The project was abandoned by the Russian Federal Space Agency after the failed deployment of the Znamya 2.5.[7]
Dude, I read about it in a 1990 donald duck (true actually, +/- some years).
can I buy sunlight to point at someone I don’t like for say, a month? no reason.
This. This I could get behind.
my neighbor ran a jackhammer for three months every day trying to build a pool. I say three months of no darkness at night is fair retribution.
You better hope you’re not a customer’s neighbor.
Ah yes, let’s redirect sunlight ONTO the Earth instead of away from it. Global warming isn’t real, after all.
/s
No way this doesn’t end poorly. I’m envisioning the SOL laser from Akira.
I imagined Mr Burns blocking out the sun, charging for sunlight.
Also I thought about who I would deliver middle of the night sunlight to, definitely not out of spite.
Unless it has AI I’m not interested
Hahahahah-
Wait… They’re serious?
Does anyone really think this could actually work? A LEO satellite would have to be massive (>1 km) to reflect a significant amount of sunlight, and you’ll need to put it waaay higher to avoid atmospheric drag. Not to mention the problem of the satellite only being above a given location for a few minutes a couple times a day.
This right here. Never mind the dystopian Mr. Burns style subscription based sunlight control bullshit that’s inherent to the very idea. That’s just to sucker in the investors who won’t know any better. Not enough people are talking about this.
I guess they could try to put the thing into some kind of geosynchronous orbit, but essentially the surface area of their mirrors will have to be equivalent to the area on the ground they plan to illuminate in order to achieve “sunlight” levels of illumination. There’s no way around that. So motherfuckers are going to start spouting off about “parabolic dishes” and “lenses” and shit any minute now. This is a red herring. No amount of optics can overcome the fact that the amount of light you can reflect will never be more than the amount of light that hits the mirror. Period. You cannot, now or ever, defy the laws of physics.
The International Space Station is basically the biggest thing we’ve ever managed to permanently put into orbit, yeah? And you can barely see it with the naked eye in the night sky, let alone measure any meaningful amount of light reflected off of it hitting any square inch of ground anywhere, with any instrument you can come up with. And it’s covered in reflective shit already – in fact, most manmade orbital objects are, in order to prevent the direct sunlight baking the fuck out of them in the vacuum of space where they can’t rely on the atmosphere to carry the heat away.
At best, even if they manage to deploy a massive Mylar foldable mirror in orbit that’s hundreds of feet across, they’re only going to be able to light up a small patch of dirt like wussy old moonlight, and even then they’ll only be able to do it in one place. Adding more targets will by necessity divide the light output in a linear fashion even if they somehow make it work like a huge DLP mirror array.
This simply can’t work.
It’s certainly a stupid idea if your trying to illuminate at the suns level, but if you wanted an area to have permanent moonlight? Not so unreasonable.
The moon is 400,000 times dimmer, so 1km^2 of mirror, which is ridiculous, could illuminate an area the size of Germany.
New York metro area is 12,000km^2, which would only need a mirror 173m on each side.
Actually might not be a bad tourist attraction for a crazy city, permanent artificial moonlight.
Granted, but if moonlight level is all you want I can already illuminate my surroundings to that benchmark with the flashlight in my pocket. We don’t need to park shit in space to accomplish that. And as a matter of fact, we already tried the “illuminate the entire town like the moon” model in the past as well. It turned out that even on a terrestrial scale it wasn’t actually a great idea because, you know, people in the vicinity who want to maybe turn it off… can’t. (Except in the latter case, maybe with the aid of a rifle.)
I am positive this is just an investor scam of some kind. If anyone is actually stupid enough to launch anything towards this end, it’s a mathematical certainty that they will be murdered in the street by either an amateur astronomer or a chiropterologist. It’ll be a toss-up who gets to him first.
Some calculations:
In a 1000km orbit, you’ll need a mirror about 9km across to appear 0.5° in diameter from the ground (the same size as the Sun), and therefore light up an area with the same illumination as the Sun.
Note that you can’t make due with a smaller mirror focused to a tighter area, as the brightest thing the mirror can reflect is the Sun, and so it must appear at least as large as the Sun in the sky to illuminate any point on the ground by the same amount.
With the much dimmer goal of moonlight illumination levels, the mirror shrinks to 9km / sqrt(400,000) = 14.2m in diameter, which is actually rather reasonable. However it would only illuminate an area 0.5° wide from the mirror’s point of view, or around 9km. And because the mirror is orbiting at 7.4km/s, you’d only get a second or two of illumination.
TLDR: Moonlight mirror 14m across, could light up a 9km diameter area for a little over a second.
Edit: In the case of a permanent mirror in geostationary orbit, a 500m mirror could provide moonlight illumination to an area around 300km in diameter.
While it would be cool for it to appear the size of the moon, it is not necessary with a shaped mirror.
You can keep the same size in a higher orbit, maybe even geosynchronous, then sync the rotation of the mirror to keep it pointing in the same spot on earth.
Granted a shaped mirror that size would be much harder to put into orbit than a flat mirror.
The 9km mirror I’m referencing is for a sunlight level of illumination; the moonlight mirror needs only be 14m in diameter (or 500m for geostationary orbit).
Until it gets cloudy, foggy, or even just a little hazy anyway.
You mean the moon?
Anyone know someone that has bought into this? I’ve got some magic beans and a bridge to sell them,
The catch is that the reflected sunlight from a small area on the reflector will be spread over a very large area by the time is reaches earth, so the energy each panel could collect is to small to make economic sense.
Yeah ok but the video… Explain that!
Venture capital is composed of in no small part ignorant jackasses playing with other people’s money.
Jackasses playing with ignorant people’s money*
This has some real futurama wormstrom energy to it.
Can I pay to point the sun at someone who is making my life miserable? Preventing them from getting a good night’s sleep will surely make things better, right?













