not sure why i found this fascinating. i was working a geospatial mapping project and stumbled on this tangent
Hexagon are bestagon
The Pentagon would like to know your location.
Go away Pentagon! Why is the Pentagon afraid of the Heptagon? Because the Heptagon octagoned the Nonagon.
octagonized?
You mean, because he is the
badumm ts
OCTAGONIST ???
I love that I can count on this being commented whenever hexagons are mentioned 💕

This paper says nothing about the “brain’s navigation system”. It is focused on the distribution of cone photoreceptors in the retina, and more precisely in the fovea.
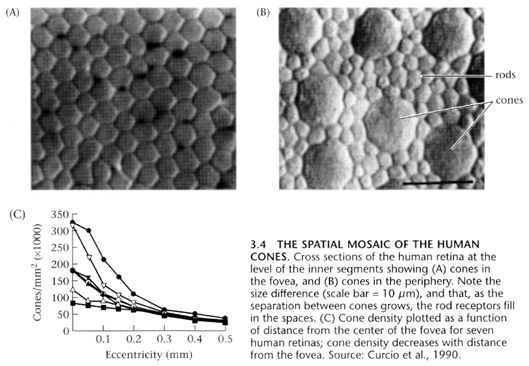
They are indeed organized in a hexagonal mosaic as you can see in the picture, and the authors present a new method to estimate spatial distribution of said cones, showing that there are anisotropies, with the cones having a larger local spacing along the horizontal axis.
The fovea (A) is the central-ish region of the retina, and it is packed with cones, which are specialized in color recognition. As you move to the periphery of the retina (B), another type of receptor becomes dominant : the rods. They are a lot better at sensing light but can’t tell which color it is. That’s why our peripheral vision is mostly shades of gray, even if your brain tries to convince you otherwise by adding the colors from context.
Anyway, not saying this isn’t an interesting topic, but it’s not the best source to illustrate it.
there was a second reference link for navigation piece:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1598543
i took both links from this paper
Find a more efficient packing pattern.
It makes sense because the real world is isotopic. Rectangular is presumptuous to some extent where high frequency information will be found.
I understand each of those words.
He’s just trying to sound smart. Lol
My dude I have like five publications in the space. But yeah I’m just some guy on the Internet. I just wish I had more opportunities to talk about it.
It started in high school when I had a side job catching dragonflies. They did experiments on their eyes, which have a hexagonal shape. It was being done to research new imaging systems. Later on I worked on some of the mathematical theory for image processing operations.
I would like to identify those specific operations but I’m pretty much the only guy who would turn up in the search results, so I’m not sure how much more specific I can get. It is unfortunate.
Cool RP bro.
What’s really cool as that the basis of support in the frequency domain has the same shape as your sampling function.
And generally speaking, the perfect shape would be a circle because you can fit the maximum amount of bandlimited noise into that space. Orientation really shouldn’t matter. It’s stranger that it does.




